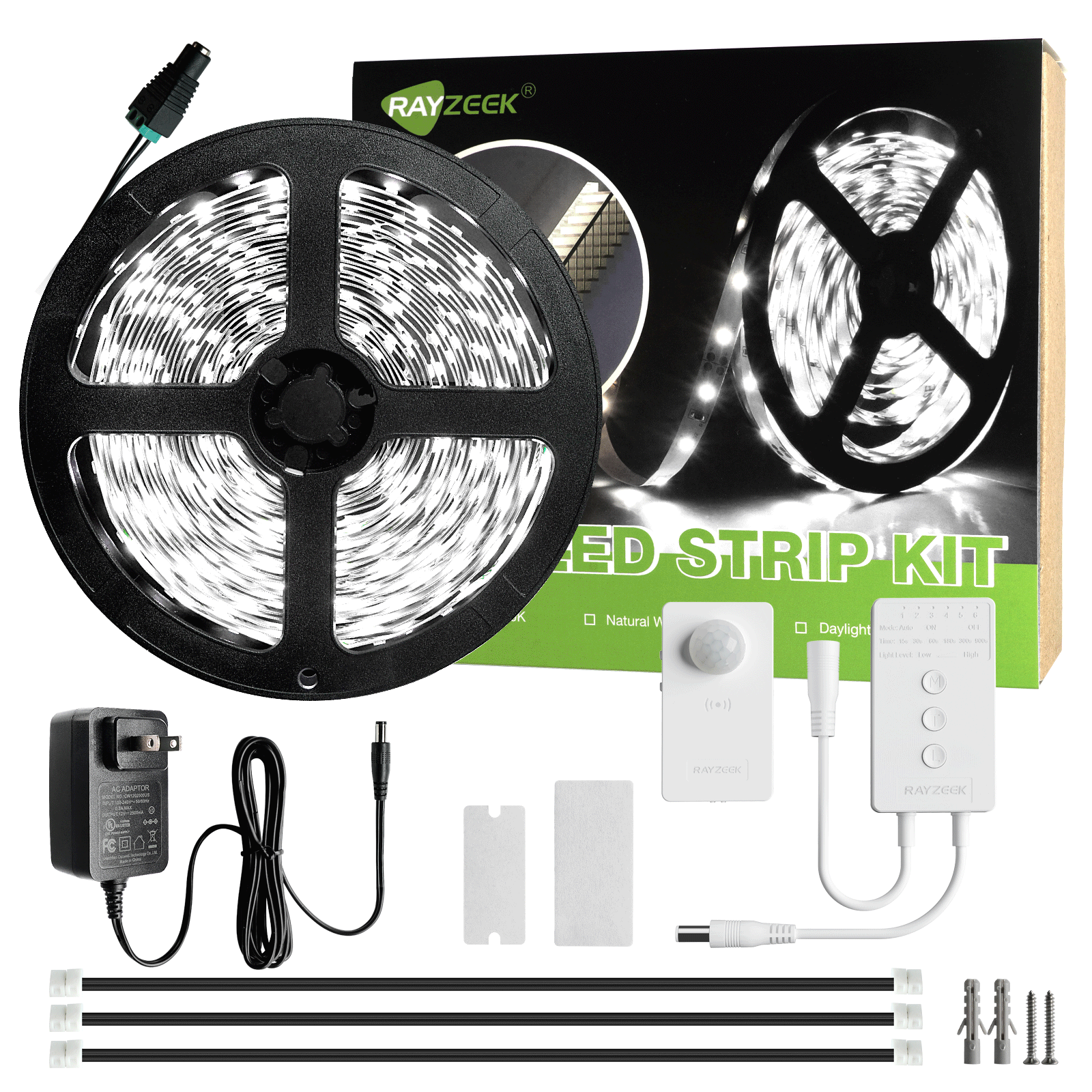
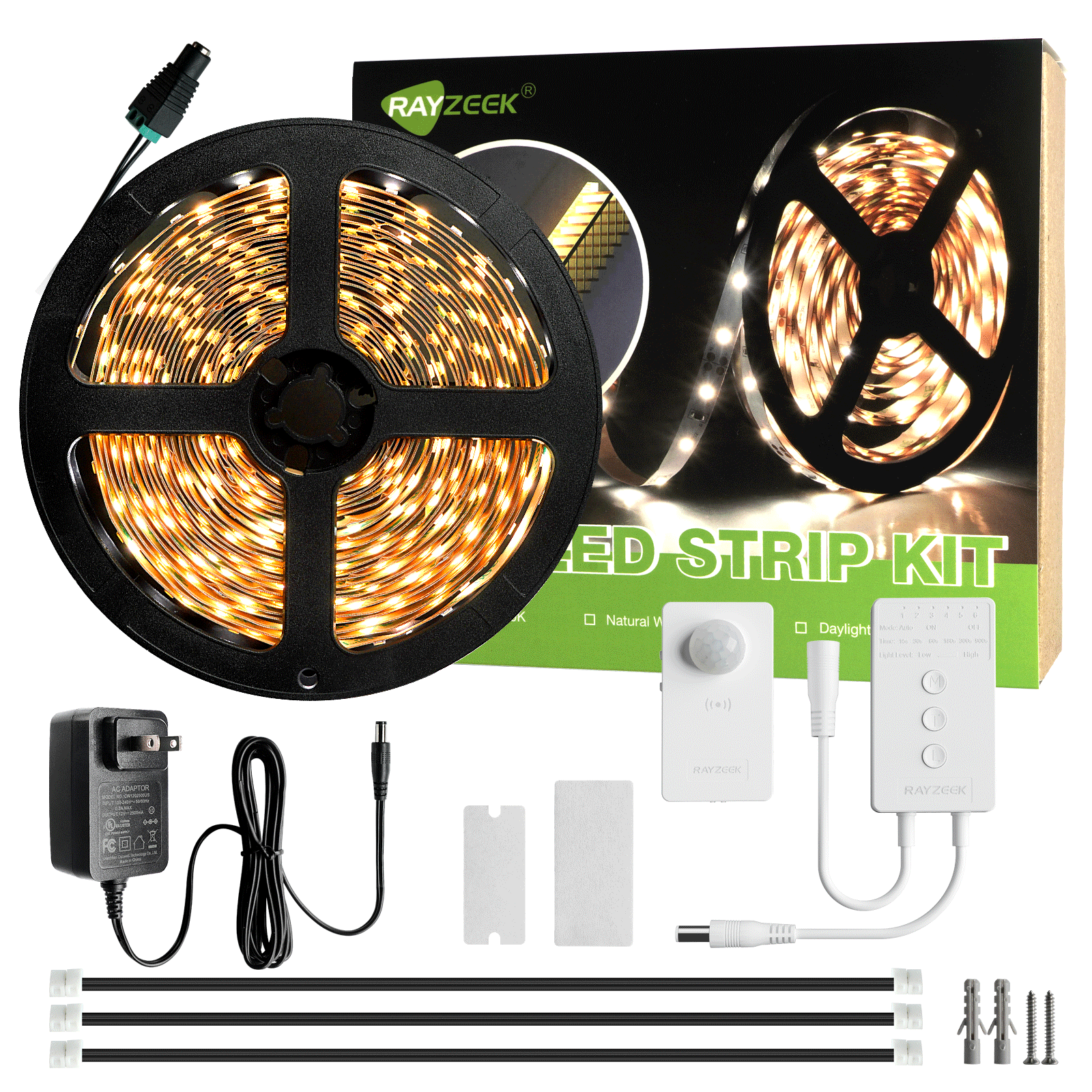
What is Light Emitting Diode (LED)
A Light Emitting Diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that converts electrical energy into light energy. It operates based on the principle of electroluminescence, where the recombination of electrons and holes within the semiconductor material releases energy in the form of photons. This emission of light occurs when an electric current passes through the LED.
LEDs are designed as heavily doped p-n junctions, allowing current to flow in the forward direction while blocking it in the reverse direction. The color of the light emitted by an LED is determined by the specific semiconductor material used and the level of doping. By controlling these factors, LEDs can emit light across a wide range of colors, including red, green, blue, and even white.
Maybe You Are Interested In
LEDs have gained popularity in the lighting industry due to their numerous advantages. They are highly energy-efficient, consuming significantly less power compared to traditional incandescent or fluorescent lights. LEDs also have a longer lifespan, making them more durable and cost-effective. Additionally, they are resistant to shock, vibration, and extreme temperatures, making them suitable for various applications.
LEDs are typically encapsulated with a transparent cover, which not only protects the LED from external factors such as dust and moisture but also helps shape and direct the emitted light. This encapsulation process allows for greater control over the light output and enables the design of various lighting fixtures.
Looking For Motion-Activated Energy-Saving Solutions?
Contact us for complete PIR motion sensors, motion-activated energy-saving products, motion sensor switches, and Occupancy/Vacancy commercial solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why Do My LED Bulbs Burn Out So Fast
LED bulbs have a lower heat output compared to other bulbs, but this also means that they can be more susceptible to overheating. This sensitivity to overheating can result in a shorter lifespan for the bulbs. To prolong the life of your LED bulbs, it is important to keep them cool. Additionally, make sure that the bulbs you are using are the appropriate size for the fitting.
What Shortens the Life of an LED Bulb
An LED bulb’s lifespan can be shortened by the temperature of its bulb case. If the temperature exceeds 85 degrees, the lifespan of the bulb is likely to decrease. Additionally, if the bulb case temperature reaches above 105 degrees, the LED light will cease to function.
Where Should You Not Use LED Bulbs
Enclosed fixtures that do not provide adequate ventilation can significantly impact the temperature of LED bulbs, leading to overheating and a reduced lifespan. This is why certain bulbs come with a warning against using them in enclosed ceiling fan or fully enclosed porch light fixtures.
How Do You Tell if a Light Bulb Is LED or Incandescent
To determine if a light bulb is LED or incandescent, you can easily identify it by checking the labeling on the packaging or the base of the bulb. This information will clearly indicate whether it is an LED bulb or not. Recognizing LED bulbs is a simple and effective method to conserve energy and minimize your environmental impact.
Which Type of LED Light Is Best for Home
2700 to 3000 Kelvins: Commonly referred to as soft white, LED lights within this range emit a warm, yellowish hue. Soft white lights are ideal for creating a comfortable and cozy atmosphere in living spaces like bedrooms, dining rooms, or living rooms.
How Long Do LED Lights Last
One of the major benefits of LED light fixtures is their long lifespan. Unlike incandescent light bulbs that typically last around 1,000 hours, the most durable LED light fixtures have been proven to last up to 100,000 hours. On average, LED light bulbs can go without replacement for at least 20 years.
Do LED Lights Get Hot
Yes, LED lights can generate heat, especially with new technology LED lighting. However, the temperatures are much safer compared to traditional lighting options. Additionally, while LED lights do emit some ambient heat, it is significantly less than what is produced by old incandescent lighting.
What Happens if LED Light Goes Out
LED bulbs do not burn out suddenly like regular bulbs when they lose power. Instead, LED bulbs gradually deteriorate over time. After a few years, their brightness diminishes, a phenomenon referred to as “luminous decay.” When they start emitting faint light, it indicates that it is time to replace them.
Why Do My LED Lights Only Work When I Touch Them
LED lights may only work when you touch them due to the fact that many LED lights and strips do not require a significant amount of voltage. This implies that the energy emitted from your body could potentially be sufficient to activate the LED light.
Why Are My LED Light Bulbs Flickering and Burning Out
Another common cause of flickering in LED bulbs is loose connections or circuits. To resolve this issue, simply tighten the LED bulb securely. Additionally, if there is a significant amount of dust in the fixture, it is advisable to blow out the connection points to remove the dust before reinserting the bulb.
Are LED Lights AC or DC
LED lights, which stands for Light Emitting Diode, are semiconductor devices that have the capability to convert electricity into light energy. As a result, LED lights operate on low DC voltages and cannot be directly connected to an AC mains supply like traditional incandescent light bulbs.
Does LED Save More Electricity
Although previously used primarily for indicator and traffic lights, LEDs are now the most energy-efficient and rapidly advancing lighting technology for general illumination purposes. They consume up to 90% less energy and have a lifespan up to 25 times longer than traditional incandescent bulbs.
Why Don’t LED Bulbs Work in My Fixture
The reasons for LED bulbs not working in your fixture can vary greatly, ranging from issues with the power source to problems with the bulb itself. Common reasons include a defective power supply, loose connections, a flawed circuit design, or even damage caused by water entering the fixture due to rain.
What Voltage Is Required for LED
LEDs are specifically designed to operate on low voltage, typically ranging from 12 to 24 volts, and require direct-current electricity. However, it is important to note that most electrical outlets supply higher voltage, typically ranging from 120 to 277 volts, and provide alternating current electricity. To ensure compatibility, an LED driver is used to convert the higher voltage, alternating current to the required low-voltage, direct current for the LEDs to function properly.