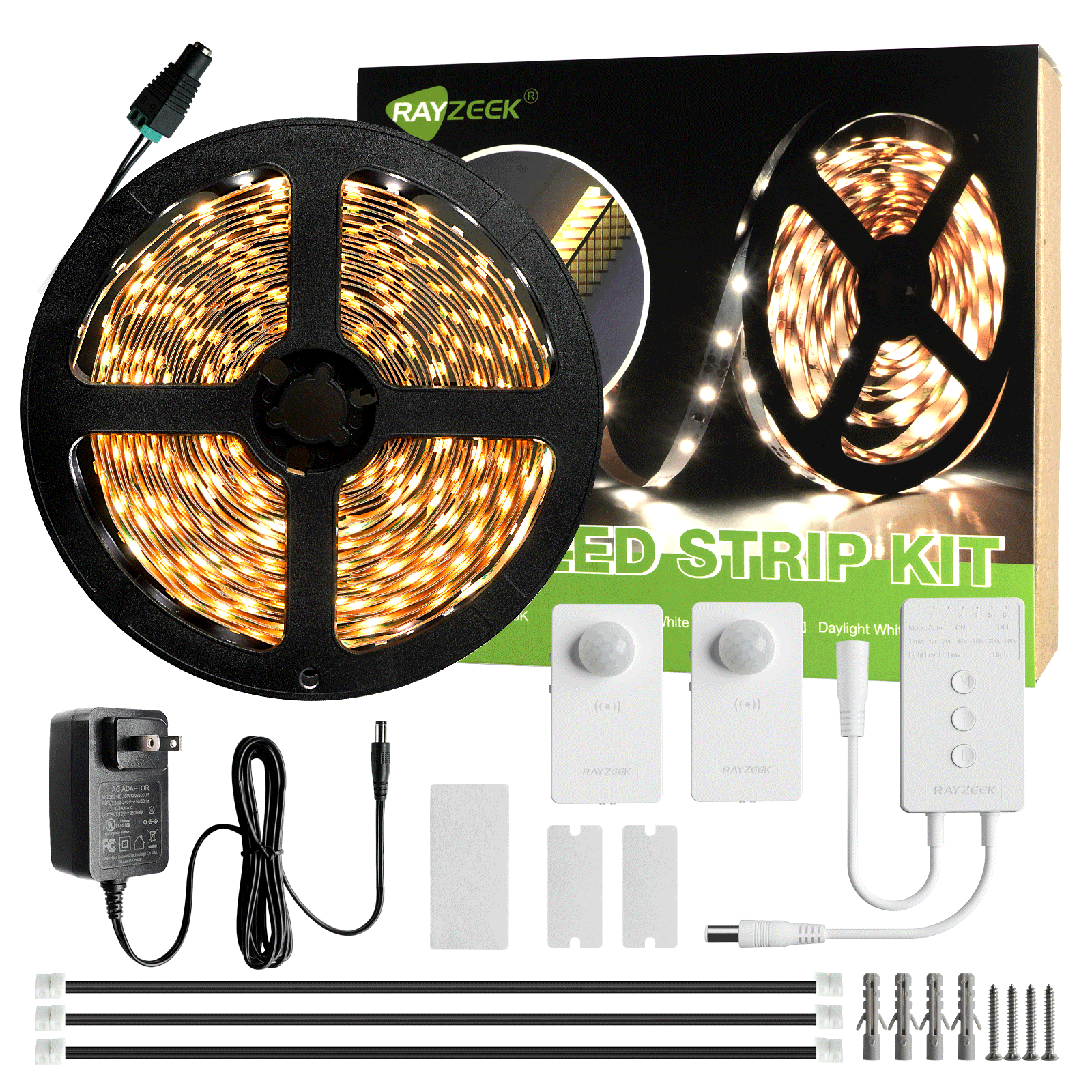
Motion sensors and presence sensors both have their unique functionalities and applications, but how do they differ? And more importantly, which one is the right choice for your specific needs? In this article, we’ll be explaining how they work, their key differences, and their various applications. We’ll also provide you with essential considerations to keep in mind when choosing between the two.
Table of Contents
- What is a Motion Sensor
- How Motion Sensors Work
- What is a Presence Sensor
- How Presence Sensors Work
- Difference Between Motion and Presence Sensors
- Applications of Motion and Presence Sensors
- Considerations When Choosing Between Motion and Presence Sensors
What is a Motion Sensor
A motion sensor, often referred to as an infrared sensor, is an electronic device that serves as a cornerstone in home security systems, automation systems, and energy-saving technologies. It’s designed to detect physical movement within a designated area by emitting or sensing various forms of energy, such as infrared radiation, radar waves, or sound waves.
The primary role of a motion sensor is to detect any form of movement in its vicinity, including people, animals, and objects. It accomplishes this by employing different technologies to identify changes in the environment. For instance, some motion sensors use infrared technology to measure the heat changes caused by moving bodies, while others use microwave or ultrasonic technology to detect changes in sound or radio waves.
Upon detecting movement, a motion sensor can also send a signal to the connected control panel of your security system or other connected devices. This can trigger a variety of responses, such as setting off an alarm, turning on lights, or adjusting the thermostat, making motion sensors a vital part of home security setups and energy-saving applications.
While motion sensors are proficient at detecting movement, they don’t necessarily identify what or who is moving. This means they can’t differentiate between a human, a pet, or a moving object, which can sometimes lead to false alarms. To counteract this, some advanced motion sensors come equipped with features like pet immunity.
How Motion Sensors Work
The inner workings of motion sensors are intriguing and vary based on the type of sensor. There are several types of motion sensors, each employing a unique method to detect movement. The most common types include Passive Infrared (PIR), Microwave, Ultrasonic, and Dual Technology sensors.
Passive Infrared (PIR)
PIR sensors are the most frequently used type of motion sensor. They function by identifying the heat emitted by an object, typically a human body. When a warm body like a human or animal passes in the detection field, it detects the change in infrared energy levels and triggers the sensor.
Microwave
Microwave sensors emit microwave pulses and then measure the reflection of a moving object. They cover a larger area than PIR sensors, but they are more expensive and can be prone to electrical interference. The sensor is activated when the echo-response of the microwave pulses is shortened due to the movement of an object.
Maybe You Are Interested In
Ultrasonic
Ultrasonic sensors emit ultrasonic sound waves, which bounce off objects and return to the sensor. When a moving object disrupts these waves, the sensor is triggered.
Dual Technology
These sensors combine two different types of technologies, usually PIR and microwave. The sensor is only triggered when both sensors detect motion, which helps to reduce false alarms.
Beam and Photoelectric Sensor
Another type of motion sensor is the beam and photoelectric sensor. This type relies on a focused beam of energy transmitting between a sensor and an emitter. If an object interrupts the energy beam, breaking it, the sensor triggers a reaction.
Once the sensor is triggered, it sends a signal to the control panel, which then performs the pre-determined action, such as turning on a light, sounding an alarm, or sending a notification to your smartphone.
Motion sensors don’t “see” motion the way humans do. Instead, they detect changes in the environment, such as changes in heat or sound waves, to determine if there’s movement. This is why they can sometimes be triggered by things like changes in temperature or air currents.
What is a Presence Sensor
A presence sensor, often referred to as an occupancy sensor, is a sophisticated device engineered to detect the presence of individuals within a designated area. Its capabilities extend beyond merely detecting movement, as it can ascertain if a person is present in a room, even if they are stationary.
These sensors utilize a variety of technologies to detect human presence. The most prevalent types include Passive Infrared (PIR), Ultrasonic, and Dual-technology sensors. PIR sensors detect the heat emitted by a human body, Ultrasonic sensors use sound waves, and Dual-technology sensors combine both methods for increased accuracy. Additionally, contemporary presence sensors rely on millimeter-wave (mmWave) technology, a form of radar technology that sends out signals and looks for reflections.
Presence sensors are crucial in smart home systems and commercial buildings, where they efficiently manage lighting, heating, and cooling systems. Upon detecting a person in a room, a presence sensor can trigger the lights to turn on, adjust the temperature, or even activate security systems. When the person leaves, the sensor can then turn off or adjust these systems, thereby saving energy and enhancing security.
These sensors are also integral components of a building’s Internet of Things (IoT) network, providing valuable information to key systems. The data from these sensors can be used to understand employee habits and behavior, detect workspace usage and occupancy, and monitor and control air quality, heating, and cooling. This information aids leadership teams in making building management more efficient and the employee experience more seamless.
How Presence Sensors Work
Presence sensors utilize a blend of technologies, primarily Passive Infrared (PIR) and Ultrasonic, and in some instances, millimeter-wave (mmWave) technology.
Passive Infrared (PIR)
PIR-based presence sensors are designed to detect the heat emitted by humans. Given that every human body emits infrared radiation, these sensors pick up changes in this radiation when an individual enters or exits a room, thereby determining their presence or absence. Certain PIR sensors are tailored for specific applications, such as desk sensors that monitor desk usage in real-time, or door-counting sensors that track the usage of a particular room. They are particularly effective in smaller spaces and can even be utilized to manage hygiene in facilities like bathrooms by tracking usage frequency.
Ultrasonic
Ultrasonic presence sensors function by emitting ultrasonic waves. When an individual enters the room, these waves bounce back to the sensor at a different frequency due to the Doppler effect. The sensor detects this change in frequency, identifying the presence of an individual. Ultrasonic sensors are often employed for security purposes and can serve as an alternative to PIR sensors in the workplace.
Millimeter-wave (mmWave)
Some contemporary presence sensors utilize mmWave technology, which is based on radar technology. These sensors send out signals and look for reflections, providing another method of detecting the presence of people.
Presence sensors can be configured with weight and size parameters to prevent unnecessary activation, making them more efficient than motion sensors in certain applications. For instance, a simple movement of a chair would trigger a motion sensor, but a presence sensor would only be activated by the presence of a person.
Once a presence sensor detects an individual, it sends a signal to the control system. This signal can trigger various actions, such as turning on lights, adjusting the thermostat, or activating security systems.
Presence sensors are designed to detect even the slightest movement, including activities like typing or reading, which might not be picked up by a standard motion sensor. This makes them ideal for situations where people may be stationary for extended periods, such as in an office or a library.
In addition to PIR and Ultrasonic sensors, there are also Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) Beacons and Optical Sensors. BLE Beacons transmit a universally unique identifier to nearby devices with a compatible app, making them useful for marketing purposes. Optical Sensors, on the other hand, use computer vision technology and artificial intelligence to provide detailed insights into person count, active occupancy, and passive occupancy, offering invaluable data for decision-making processes.
Get Inspired by Rayzeek Motion Sensor Portfolios.
Doesn't find what you want? Don't worry. There are always alternate ways to solve your problems. Maybe one of our portfolios can help.
Difference Between Motion and Presence Sensors
While motion sensors and presence sensors share similarities, they possess distinct differences that make them suitable for different applications.
Detection Mechanism
Motion sensors are designed to detect significant movement within their field of view. They respond to changes in the environment, such as a person entering a room. In contrast, presence sensors are more sensitive, capable of detecting even the slightest movements or changes in body temperature. They can sense if someone is sitting still in a room, a scenario that motion sensors might miss.
Sensitivity
Presence sensors operate with higher image resolutions, making them more sensitive than motion sensors. They can detect subtle changes in the environment, such as the heat emitted by a human body, providing a more accurate reading of the situation. On the other hand, motion sensors require more substantial movement to be triggered and may not detect small or slow movements.
False Alarms
Presence sensors, due to their high sensitivity, may trigger more false alarms compared to motion sensors. They could be activated by a pet or even changes in temperature. Motion sensors, focusing on larger movements, are less likely to give false alarms.
Energy Efficiency
Presence sensors contribute to greater energy efficiency. Since they can detect even a stationary person, lights or HVAC systems can remain on as needed, avoiding unnecessary energy usage. In contrast, motion sensors might turn off systems when a person is still in the room but not moving, leading to potential discomfort and energy waste when systems are restarted.
Application
Motion sensors are commonly used in security systems to detect intruders moving around. Presence sensors, with their ability to detect stationary individuals, are more suited for occupancy monitoring and energy management systems, such as smart lighting or HVAC control.
Technology
Both motion and presence sensors utilize a variety of technologies. Motion sensors often use infrared, microwave, or ultrasonic technology to detect moving objects. Presence sensors, on the other hand, may use technologies like pressure sensors, proximity sensors, photoelectric sensors, and video sensors to detect the presence of people, even when they are stationary.
Applications of Motion and Presence Sensors
Motion and presence sensors, with their diverse functionalities, find applications across a multitude of sectors. Their use can be customized to cater to the specific needs of a space or situation. Let’s delve into some of the key uses of these sensors.
Home Security
Motion sensors are a cornerstone of home security systems. They detect movement and set off alarms or send notifications when they pick up unusual activity. On the other hand, presence sensors can keep track of family members, sending alerts when children or elderly relatives move in or out of certain areas of the home.
Energy Efficiency
Both types of sensors contribute significantly to energy conservation. Motion sensors control lighting, activating lights when movement is detected and deactivating them when a room is unoccupied. Presence sensors, on the other hand, maintain lighting as long as someone is present in the room, even if they’re stationary, preventing unnecessary energy usage.
Healthcare
Presence sensors are particularly beneficial in healthcare settings, where they can monitor patients, especially those with mobility issues or dementia. They can alert healthcare providers if a patient leaves a designated area or if there’s no movement over an extended period, indicating a potential health concern.
Retail and Business
In retail environments, motion sensors can track customer movement, providing valuable data on customer behavior and store layout effectiveness. Presence sensors can monitor and manage occupancy levels in real-time, which is useful in maintaining social distancing guidelines.
Looking For Motion-Activated Energy-Saving Solutions?
Contact us for complete PIR motion sensors, motion-activated energy-saving products, motion sensor switches, and Occupancy/Vacancy commercial solutions.
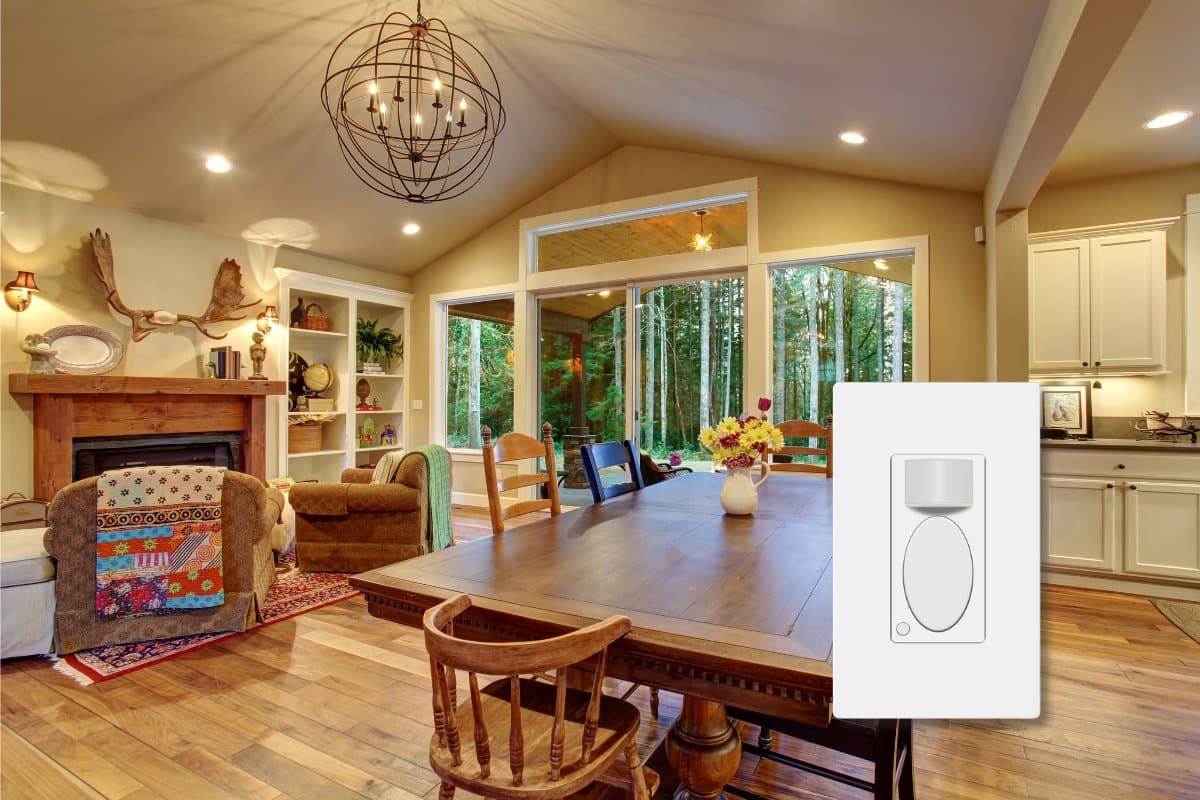
Smart Homes
In smart home setups, motion and presence sensors can automate various tasks. For example, motion sensors can trigger actions like opening a garage door or turning on outdoor lights. Presence sensors can adjust the thermostat based on whether anyone is home, enhancing comfort while optimizing energy use.
Industrial Applications
In industrial settings, motion sensors can enhance safety by detecting movement in hazardous areas and triggering alarms. Presence sensors can monitor employee presence in specific zones, aiding in access control and time and attendance tracking.
In addition to these applications, the choice between motion and presence sensors can be influenced by the layout of your home and your lifestyle. For instance, motion sensors are ideal for areas with more movement, such as hallways or staircases. In contrast, presence sensors are better suited for areas where you’re likely to be stationary, such as a home office, living room, or bedroom.
These sensors can also be used to control room functions, such as lowering the temperature of unused rooms, adding another layer of energy efficiency. In essence, the integration of motion and presence sensors can significantly enhance the functionality and comfort of your smart home setup, adapting to the way you and your family move through your home.
Considerations When Choosing Between Motion and Presence Sensors
When deciding between motion and presence sensors, several key factors should be taken into account to ensure the best fit for your specific needs. Here’s a more comprehensive look at these considerations:
Sensor Purpose
The primary factor is the intended use of the sensor. If your goal is to detect significant movement, such as for security or lighting control in high-traffic areas like hallways or staircases, a motion sensor would be the optimal choice. Conversely, if you need to detect subtle movements or occupancy in a room, such as people working at their desks or watching a movie, a presence sensor would be more suitable.
Sensitivity and Range
Motion sensors generally have a higher sensitivity and a wider range, enabling them to detect movement from a greater distance. Yet, this high sensitivity can sometimes lead to false alarms. Presence sensors, in contrast, are designed to detect more subtle movements within a smaller range, making them ideal for enclosed spaces.
Energy Efficiency
Presence sensors can significantly contribute to energy efficiency by ensuring that lights and HVAC systems are only active when a space is occupied. While motion sensors can also contribute to energy efficiency, they are typically less effective because they can’t differentiate between an occupied and an unoccupied space.
Cost
Motion sensors are usually less expensive than presence sensors. But, the cost can vary depending on the specific features of the sensor, such as its range, sensitivity, and the technology it uses. It’s crucial to consider both the upfront cost of the sensor and the potential long-term savings, particularly in terms of energy efficiency.
Installation and Maintenance
Both types of sensors require installation and may need occasional maintenance or calibration. The complexity of installation and the level of maintenance required should be considered when choosing between the two.